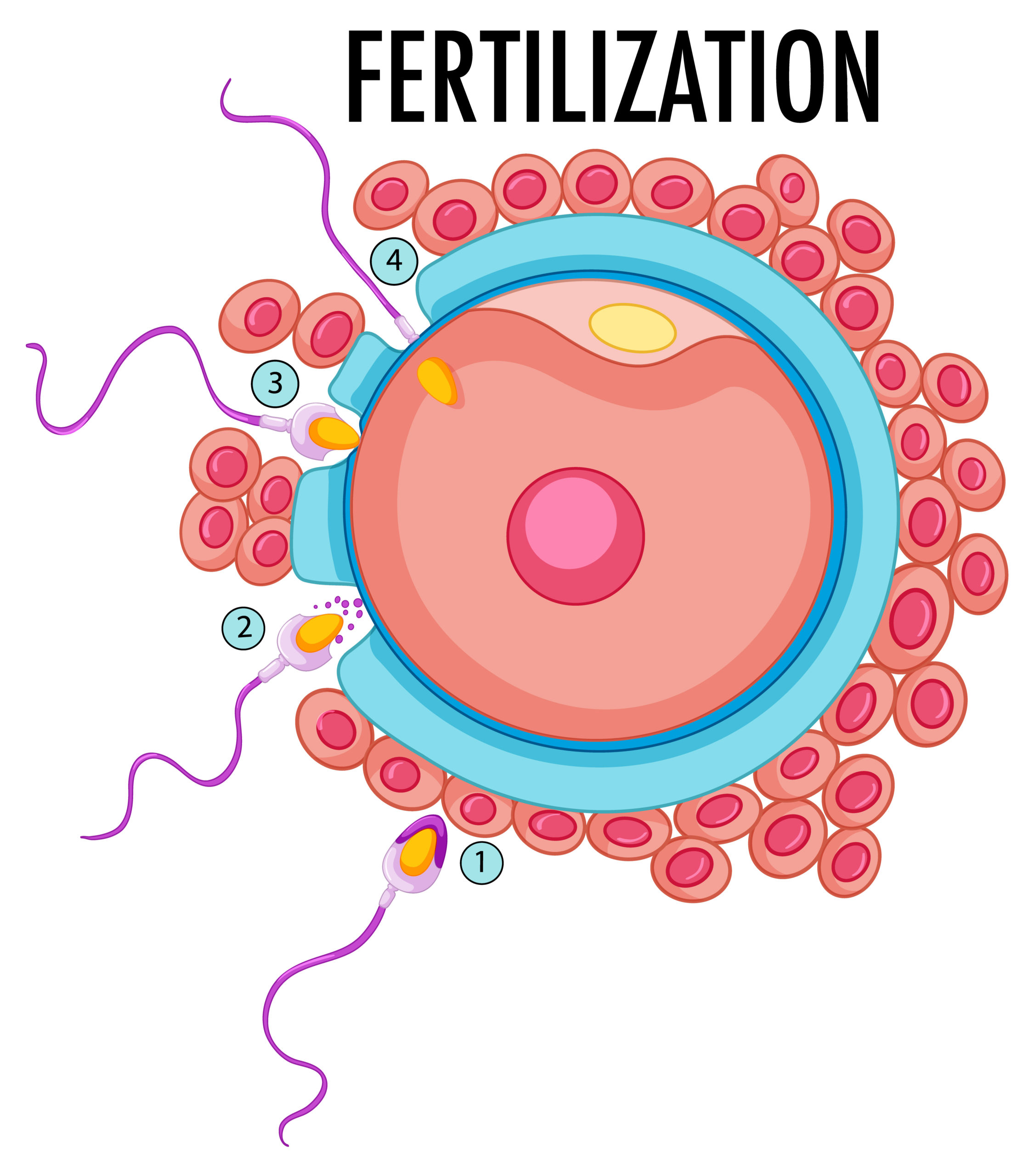
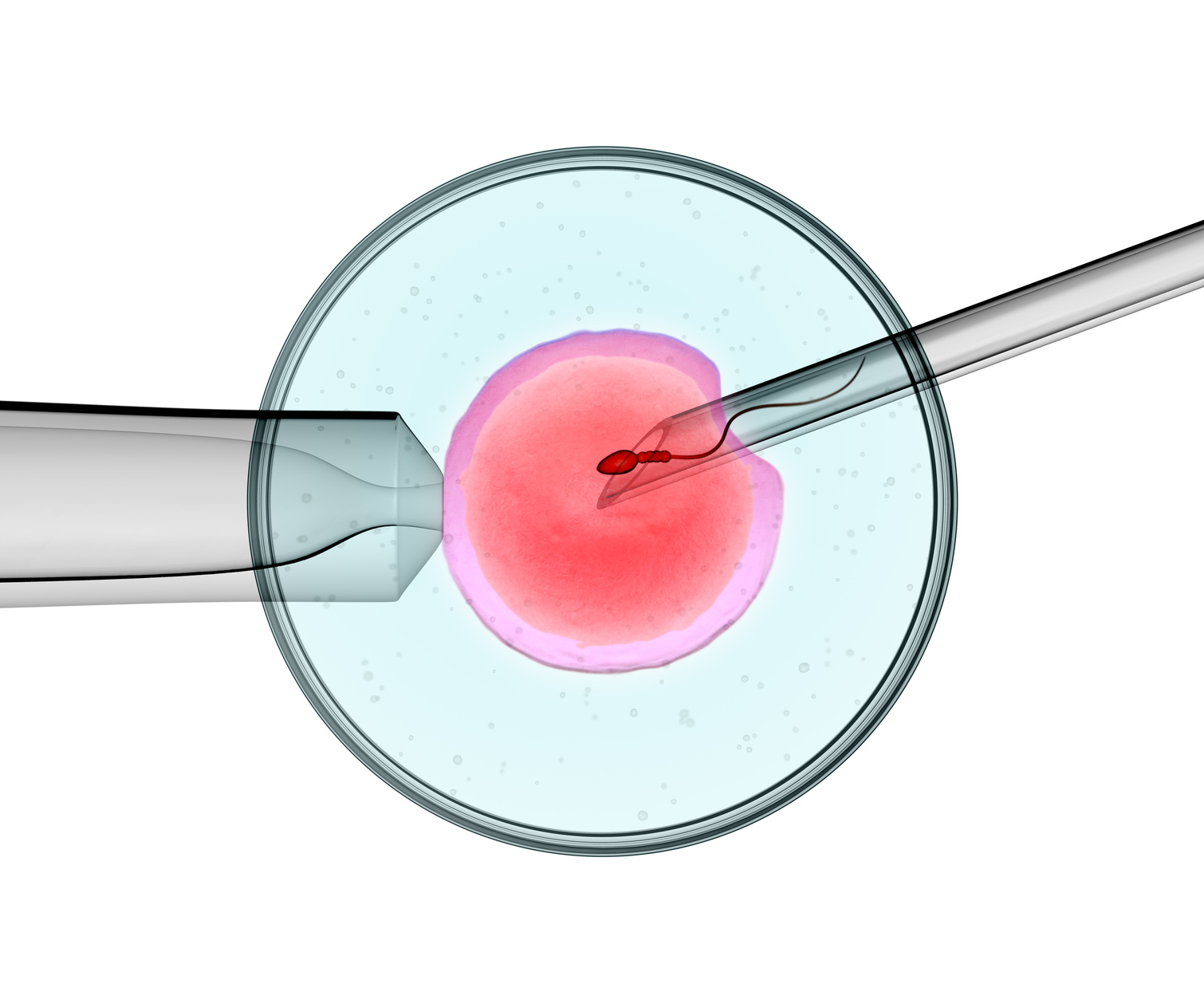
The fertilization procedure in In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a pivotal stage where the retrieved eggs and collected sperm are combined to facilitate the creation of embryos. This process occurs in a controlled laboratory environment and can be accomplished through either conventional insemination or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI).
Conventional Insemination
- Mixing Eggs and Sperm: In conventional insemination, the mature eggs retrieved from the ovaries are placed in a petri dish with a carefully prepared sample of sperm from the male partner or a donor. This process simulates the natural meeting of eggs and sperm as closely as possible within a lab setting.
- Natural Selection of Sperm: The sperm swim towards the eggs, and fertilization occurs when one sperm penetrates the outer layer of an egg. The goal is for multiple eggs to be fertilized, although not every egg will necessarily become fertilized.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
- Direct Injection of Sperm: ICSI is used in cases where there might be concerns about sperm quality or previous fertilization failures. A single sperm is selected by an embryologist and injected directly into each egg. This method significantly increases the chances of fertilization by bypassing natural barriers to sperm entry.
- Monitoring Fertilization: Post-injection, the eggs are monitored to confirm fertilization. Normal fertilization is indicated by the presence of two pronuclei in the egg.
Post-Fertilization Development
- Embryo Culturing: Once fertilization occurs, the fertilized eggs, now called embryos, are cultured in the lab for several days. During this period, they are kept in incubators that provide optimal conditions for growth.
- Embryo Assessment: Embryologists monitor the embryos to assess their development. Factors such as cell division rate and appearance are used to evaluate their viability.
- Selection for Transfer: The best-quality embryos are selected for transfer to the woman’s uterus. The remaining viable embryos can be frozen for future use.