Ovarian Stimulation
Ovarian Stimulation is a crucial step in the In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) process, designed to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs rather than the single egg typically released during a normal menstrual cycle. This increase in egg production is essential for IVF, as it raises the chances of creating viable embryos for implantation.
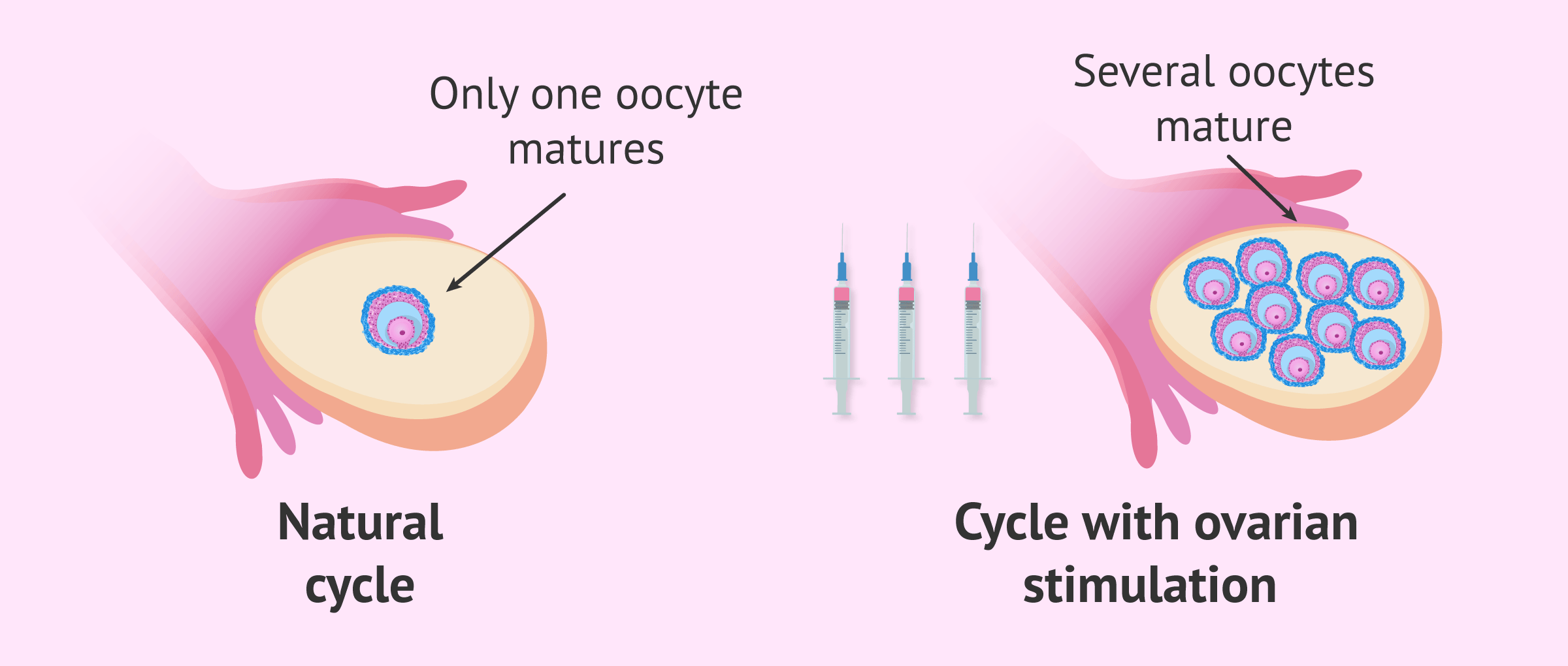

Process of Ovarian Stimulation
- Hormonal Medication: The process begins with the administration of fertility drugs containing follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), or a combination of both. These hormones stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple follicles, each potentially containing an egg.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring is essential during this phase. This usually involves blood tests to measure hormone levels and transvaginal ultrasound scans to observe the development of follicles in the ovaries. The response to stimulation can vary greatly among individuals, and monitoring ensures that the dosage of medication can be adjusted as needed to optimize egg production while minimizing the risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS), a potentially serious complication.
- Adjustment of Medication: Based on monitoring results, doctors might adjust the dosages of the hormonal medication. The goal is to achieve a balance where enough follicles are stimulated to increase the chances of a successful IVF cycle but not so many that the patient’s health is put at risk.
Duration of Ovarian Stimulation
The stimulation phase typically lasts about 8-14 days, but this can vary depending on how the ovaries respond to the medication.



