How Are Egg Donors Compensated?
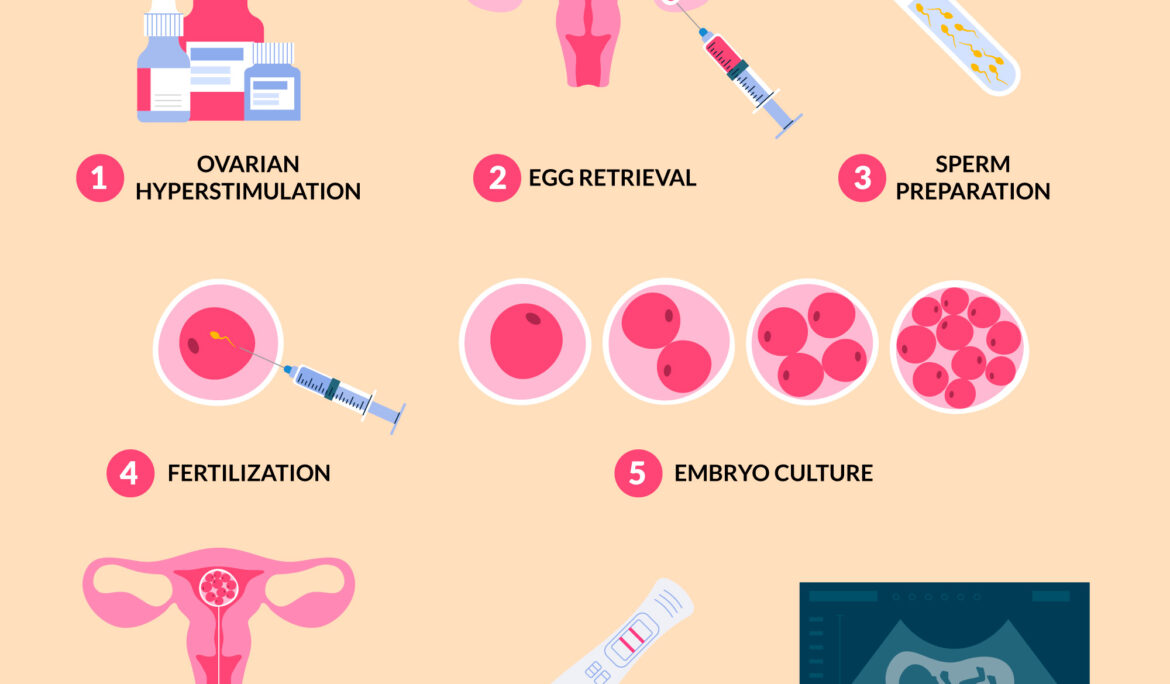

Egg donation is a crucial component of fertility treatments, offering hope to many individuals and couples struggling to conceive. For those considering becoming egg donors, one of the most common questions is, “How are egg donors compensated?” This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the compensation process, including factors that influence compensation, typical amounts, and the ethical considerations involved.
Understanding Egg Donor Compensation
Egg donor compensation is a payment made to women who donate their eggs to help others achieve pregnancy. This compensation is not only for the time and effort involved in the donation process but also for the physical and emotional demands placed on the donor.
Factors Influencing Egg Donor Compensation
-
Geographic Location:
- Compensation rates for egg donors can vary significantly depending on the location. In regions with a high demand for egg donors or where living costs are higher, compensation tends to be more generous. For example, egg donors in large metropolitan areas may receive higher compensation than those in rural areas.
-
Donor’s Profile:
- The donor’s characteristics, such as age, education, physical appearance, and ethnic background, can influence compensation. Some fertility clinics and agencies may offer higher compensation to donors who meet specific criteria, such as having a college degree or belonging to an in-demand ethnic group.
-
Number of Previous Donations:
- Experienced egg donors who have successfully donated before may receive higher compensation. This is because previous donations indicate that the donor’s eggs are viable and that she can handle the physical and emotional aspects of the process.
-
Clinic or Agency Policies:
- Different fertility clinics and egg donor agencies have their own compensation structures. Some may offer a flat fee for all donors, while others might adjust compensation based on the factors mentioned above. It’s important for potential donors to research and compare different options before making a decision.
Typical Egg Donor Compensation Amounts
-
United States:
- In the U.S., egg donors can typically expect to be compensated between $5,000 and $10,000 per donation cycle. However, compensation can go as high as $15,000 or more in certain cases, especially for donors with highly sought-after characteristics or in high-demand regions.
-
International Compensation:
- Compensation amounts vary widely across different countries. In some European countries, compensation is more regulated and may be lower than in the U.S., ranging from €700 to €1,500. In contrast, countries with less regulation might offer compensation comparable to U.S. rates or even higher.
What Does the Compensation Cover?
-
Time and Effort:
- Egg donation is a time-consuming process that includes medical appointments, hormone injections, and the egg retrieval procedure. Compensation acknowledges the time and effort donors invest in the process.
-
Physical and Emotional Demands:
- The physical demands of hormone treatments and the egg retrieval process, as well as the emotional aspects of donating eggs, are significant. Compensation reflects the commitment and potential discomfort the donor may experience.
-
Travel and Related Expenses:
- In addition to the base compensation, donors may receive reimbursement for travel, lodging, and other expenses incurred during the donation process. This is particularly common for donors who travel to another city or country to donate.
Ethical Considerations of Egg Donor Compensation
-
Informed Consent:
- It’s essential that egg donors provide informed consent, fully understanding the risks, responsibilities, and the nature of the compensation. Reputable clinics and agencies ensure that donors are well-informed before proceeding.
-
Avoiding Exploitation:
- Compensation should be fair and not exploitative. There is ongoing debate about whether higher compensation could incentivize women to donate eggs without fully considering the risks. Ethical guidelines suggest that compensation should reflect the effort and inconvenience without creating undue financial pressure on donors.
-
Regulation and Transparency:
- Different countries have varying regulations on egg donor compensation. In some places, compensation is tightly regulated to ensure ethical practices, while in others, there may be less oversight. Transparency in the compensation process is crucial for maintaining ethical standards and protecting donors.
The Process of Receiving Compensation
-
Timing of Payment:
- Compensation is typically paid after the egg retrieval procedure is completed. Some clinics or agencies may provide partial payments at different stages of the process, such as after hormone stimulation begins or following the egg retrieval.
-
Method of Payment:
- Payments are usually made via check or direct deposit. Donors should ensure that they understand the payment schedule and method before beginning the donation process.
-
Tax Implications:
- In some countries, egg donor compensation is considered taxable income. Donors should be aware of any tax implications and may want to consult with a tax professional to understand their obligations.
Conclusion
Egg donor compensation is an essential part of the egg donation process, acknowledging the significant time, effort, and physical demands involved. While compensation amounts can vary based on geographic location, donor profile, and other factors, it is crucial that the process remains ethical, transparent, and fair. Prospective donors should carefully consider their options, understand the risks, and ensure they are fully informed before proceeding.



