What is TESA? Understanding Treatment for Male Infertility
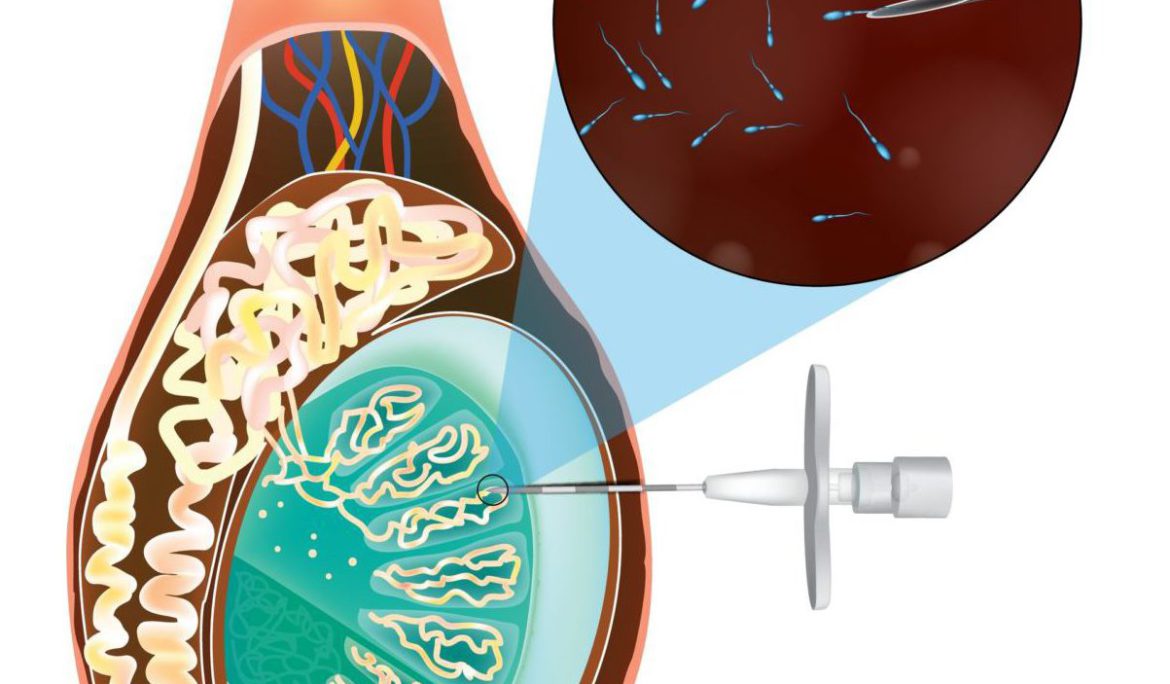

Male infertility is a challenge for many couples trying to conceive. A common underlying factor for this condition is azoospermia, a scenario where no sperm are present in the ejaculate. Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA) emerges as a beacon of hope, especially for men with non-obstructive azoospermia. This article delves into the nuances of TESA, exploring how it addresses male infertility and sheds light on who might benefit from this procedure.
What is Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA)?
TESA is a medical procedure designed to extract sperm directly from the testicle. It is typically performed under local anesthesia and involves inserting a needle into the testis to withdraw tissue. This tissue is then processed in a laboratory to extract viable sperm, which can be used in assisted reproductive technologies, such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI).
Who Needs TESA?
TESA is particularly beneficial for men with non-obstructive azoospermia, a condition where sperm production is low but there is no physical blockage in the reproductive tract. Causes of non-obstructive azoospermia include genetic conditions, hormonal imbalances, or previous surgeries. For these individuals, traditional methods of sperm retrieval are not effective, making TESA an invaluable option.
The Benefits of TESA
The primary advantage of TESA is its ability to provide a solution for men who otherwise have no sperm in their ejaculate. This procedure enables couples to pursue biological parenthood, a dream that may seem unattainable for those facing severe male infertility. Additionally, TESA is less invasive and more cost-effective compared to other sperm retrieval methods, such as Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE).
The Procedure Explained
The TESA procedure is usually quick and involves minimal discomfort. A fine needle is used to puncture the testis, and a small sample of tissue is aspirated. The sample is then taken to an embryology lab, where it is processed to isolate sperm. If viable sperm are found, they can be used immediately for fertility treatments or frozen for future use.
Risks and Considerations
As with any medical procedure, TESA carries some risks, including bleeding, infection, or damage to the testicular tissue. However, these complications are rare, and the procedure is generally considered safe. It is crucial to consult with a fertility specialist to understand the potential risks and benefits based on your individual circumstances.
Preparing for TESA
Preparation for TESA involves a thorough evaluation by a fertility specialist. This may include blood tests, hormone assessments, and imaging studies to assess the condition of the testicles. Couples are also counseled on the chances of success and the possible need for repeat procedures.
How is TESA different from TESE?
TESA and TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction) are both procedures used to retrieve sperm directly from the testicles. TESA involves aspirating tissue with a needle, while TESE is more invasive and involves making an incision in the testis to remove tissue.
Is the TESA procedure painful?
TESA is generally performed under local anesthesia, which minimizes pain during the procedure. Post-operative discomfort is usually mild and can typically be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
What are the risks associated with TESA?
While TESA is considered safe, there are some risks, including bleeding, infection, and damage to the testicular tissue. These complications are relatively rare, and the procedure is considered low-risk.
Can TESA be used for men with obstructive azoospermia?
While TESA is specifically designed for non-obstructive azoospermia, men with obstructive azoospermia (due to blockages or other issues) might undergo a similar procedure but are generally more suited for procedures aimed at bypassing or repairing the obstruction.
What happens to the sperm retrieved from TESA?
Sperm extracted through TESA can be used immediately for IVF or ICSI procedures or frozen for future use. The success of using these sperm depends on various factors, including the quality of the sperm and the partner’s reproductive health.
How successful is TESA?
The success of TESA depends on several factors, including the reason for azoospermia and the quality of the extracted sperm. When combined with IVF or ICSI, TESA can significantly increase a couple’s chances of conceiving.
How should I prepare for a TESA procedure?
Preparation typically involves a series of fertility tests, medical evaluations, and discussions with your healthcare provider. It’s important to understand the procedure, its risks, and the post-operative care required.
Can TESA be repeated if it doesn’t work the first time?
Yes, TESA can be repeated if necessary. However, the decision to undergo multiple procedures should be made in consultation with your fertility specialist, considering the reasons for the initial procedure’s outcome and the overall health of the patient.
How long is the recovery time after TESA?
Most men can return to their regular activities within a few days post-TESA, although it’s advised to avoid strenuous activities and sexual activity for a short period to allow for healing.
Conclusion
Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA) represents a significant advancement in treating male infertility, particularly for those with non-obstructive azoospermia. By offering a less invasive and effective method for sperm retrieval, TESA opens the door to fatherhood for many men. If you or your partner are facing challenges with male infertility, consulting with a fertility specialist about TESA might be a step towards realizing your dreams of starting a family.
Understanding your options is the first step towards making informed decisions in your fertility journey. TESA, combined with assisted reproductive technologies, has the potential to turn the tide in the fight against male infertility.



