Getting Pregnant With PCOS
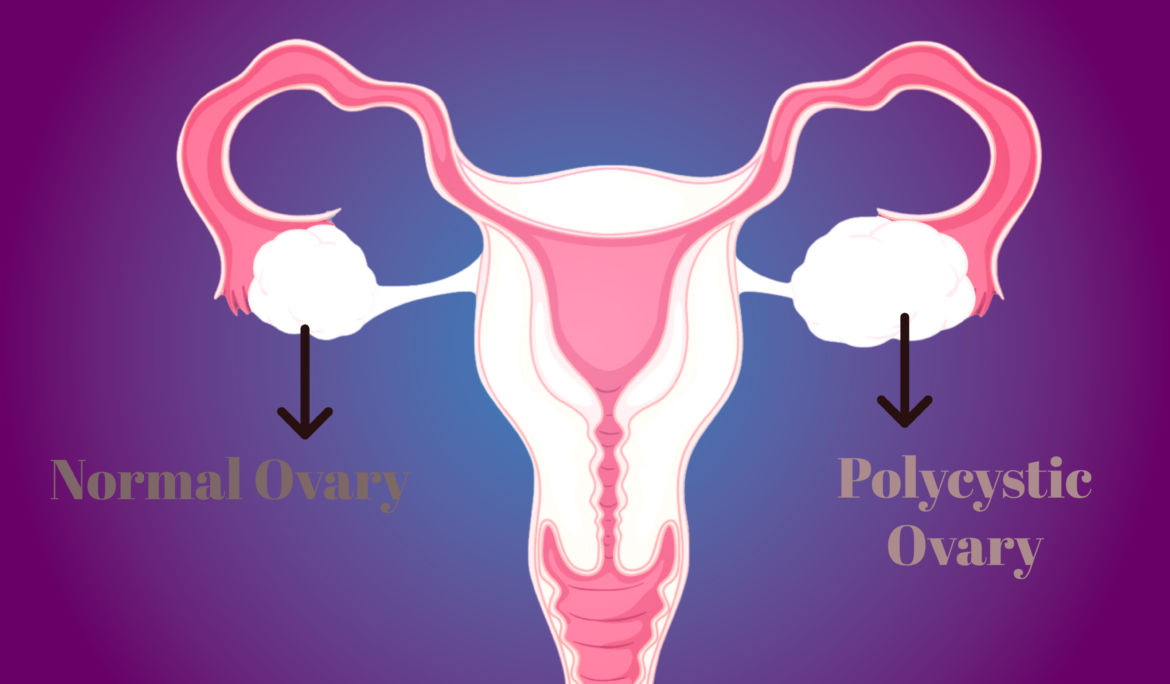

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects people of reproductive age, often causing irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and difficulties with ovulation. One of the significant challenges for individuals with PCOS is getting pregnant. However, with the right information, lifestyle changes, and medical support, it is possible to conceive and fulfill your dream of parenthood. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore strategies to enhance your chances of getting pregnant while living with PCOS.
What is POCS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects people with ovaries, primarily during their reproductive years. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, high levels of androgens (male hormones) in the body, and small fluid-filled sacs (cysts) in the ovaries, which is how it got its name. PCOS can lead to a range of health issues, including fertility challenges, insulin resistance, weight gain, acne, and excessive hair growth.
What are the causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (POCS)?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex and multifactorial condition, and its exact cause is not fully understood. However, several contributing factors are believed to play a role in the development of PCOS. These include:
- Genetics: There is a strong genetic component to PCOS. If a close family member, such as a mother or sister, has PCOS, you may be at a higher risk of developing it.
- Hormonal Imbalances: PCOS is characterized by an imbalance in sex hormones, particularly elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) like testosterone. This hormonal imbalance can disrupt the normal function of the ovaries.
- Insulin Resistance: Many individuals with PCOS also have insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This leads to increased insulin production, which can contribute to elevated androgen levels and interfere with normal ovulation.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation may be a contributing factor in PCOS. Inflammation can lead to insulin resistance and disrupt ovarian function.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity and an unhealthy lifestyle, including poor diet and lack of exercise, can exacerbate PCOS symptoms and increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Environmental Factors: Some environmental factors, such as exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, may contribute to the development of PCOS, although research in this area is ongoing.
It’s important to note that PCOS is a heterogeneous condition, meaning it can manifest differently in different individuals. Not all people with PCOS will have the same combination of symptoms or contributing factors. Diagnosis and management of PCOS typically involve addressing its various aspects, such as hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and lifestyle factors, to improve overall health and alleviate specific symptoms. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a specialist in reproductive endocrinology can help individuals with PCOS develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their unique needs.
How much does POCS reduce fertility?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can greatly reduce fertility, making it more difficult to conceive and carry a baby to full term. Approximately 70% of women with PCOS experience difficulty with ovulation, which can significantly decrease the chances of conception. Additionally, PCOS is associated with higher rates of miscarriage and increased risk of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Furthermore, the hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can lead to a variety of other fertility-related issues, such as irregular menstrual cycles, endometrial hyperplasia (thickening of the uterus lining), and anovulation (failure to ovulate).
Is IVF effective for POCS?
Yes, In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a highly effective form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) that can help individuals with PCOS overcome fertility issues. IVF involves combining an egg and sperm in a laboratory setting, outside of the body, and then implanting the resulting embryos into the uterus. This technique bypasses any potential problems with ovulation or implantation that can occur due to PCOS. Studies have shown that IVF is a successful treatment for PCOS, with many women achieving successful pregnancies.
Can I get pregnant with POCS?
Yes, it is possible to get pregnant with PCOS. With the right lifestyle changes and medical support, individuals with PCOS can increase their chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy. Making positive lifestyle modifications such as following a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, reducing stress levels, and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve fertility in women with PCOS.
What are the methods to conceive with PCOS?
Conceiving Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can be challenging, but there are several methods and strategies that can help increase your chances of getting pregnant. Here are some methods to consider:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is crucial for managing PCOS and improving fertility. Weight loss, even as little as 5-10% of your body weight, can help regulate menstrual cycles and enhance ovulation.
- Healthy Eating: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, and a diet low in sugar and refined carbohydrates. A dietitian can provide personalized dietary guidance.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate, regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of exercise per week.
- Medications:
- Ovulation-Inducing Medications: Clomiphene and Letrozole are commonly prescribed medications to induce ovulation in individuals with PCOS.
- Metformin: This medication is often used to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate menstrual cycles, which can aid in ovulation.
- Hormone Therapy:
- Oral Contraceptives: Birth control pills can help regulate menstrual cycles and manage symptoms of PCOS. However, they are not suitable when actively trying to conceive.
- Progesterone: Progesterone supplements can help induce menstrual periods and support fertility.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): IUI involves placing specially prepared sperm directly into the uterus, increasing the chances of fertilization.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a more advanced fertility treatment where eggs are retrieved, fertilized outside the body, and the resulting embryos are transferred into the uterus.
- Fertility Monitoring:
- Ovulation Tracking: Monitor your menstrual cycles and track ovulation using methods like basal body temperature charting, cervical mucus monitoring, or ovulation predictor kits.
- Fertility Apps: There are smartphone apps designed to help track your menstrual cycle and predict fertile days.
- Consult a Fertility Specialist:
- Consider consulting with a reproductive endocrinologist or fertility specialist who specializes in treating PCOS-related infertility. They can provide tailored treatment plans and guidance.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices:
- Stress Management: High stress levels can negatively impact fertility. Practicing stress reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can be beneficial.
- Smoking and Alcohol: Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as both can affect fertility.


